Objectives
- Centralize, clean and harmonize field data from different sources with minimum human effort
- Provide a digital platform with user friendly, real-time dashboard to visualize performance indicators for programs and individuals
- Identify opportunities for improvement and record decisions and actions
Description
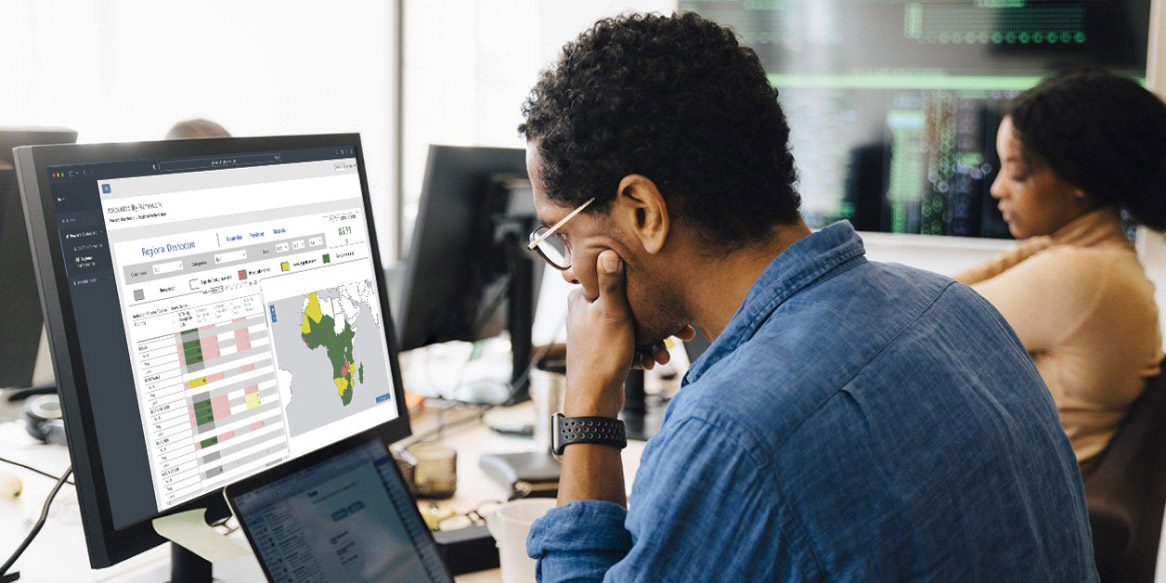
The Accountability Framework combines the automatic capture, cleaning, harmonization, and analysis of country polio activity data to produce an easy-to-use series of dashboards. As field staff report in detail on outbreak and routine interventions using diverse mechanisms, the raw data is automatically pulled from various electronic sources and aggregated into xMart repository
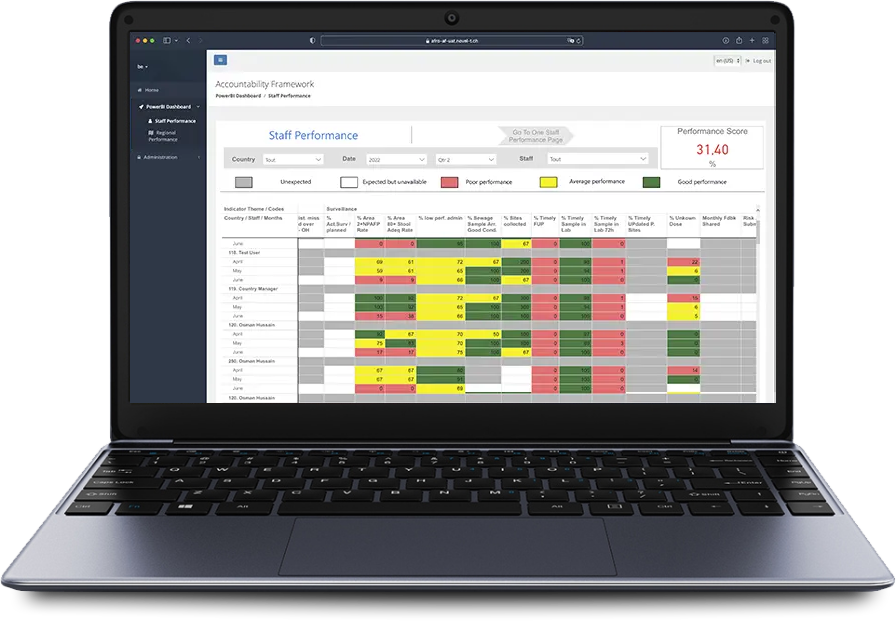
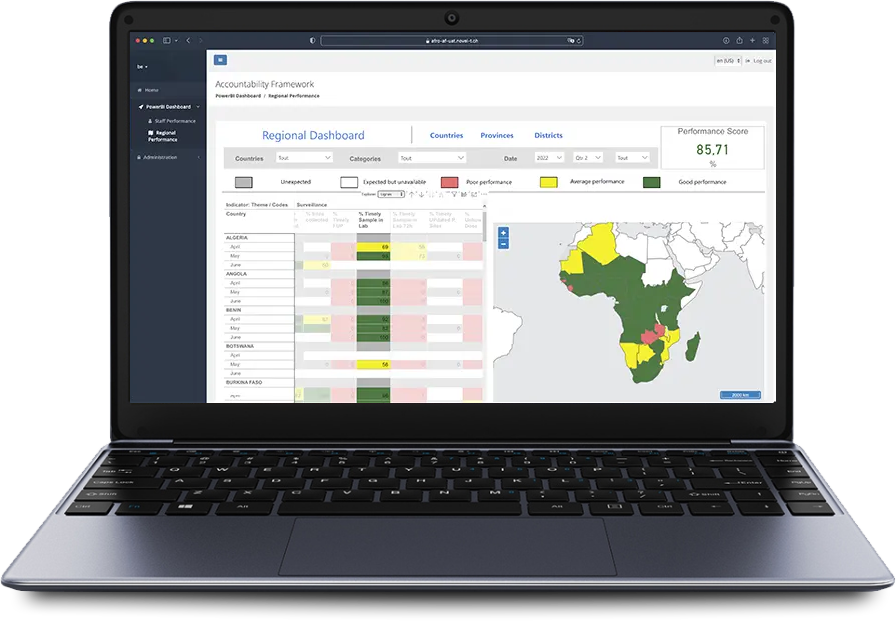
The Accountability Framework system processes data from the repository and computes scores for individual staff and program activities monthly against approved key indicators. Managers at national and regional offices can visualize performance down to district level, note decisions, and propose improvements.
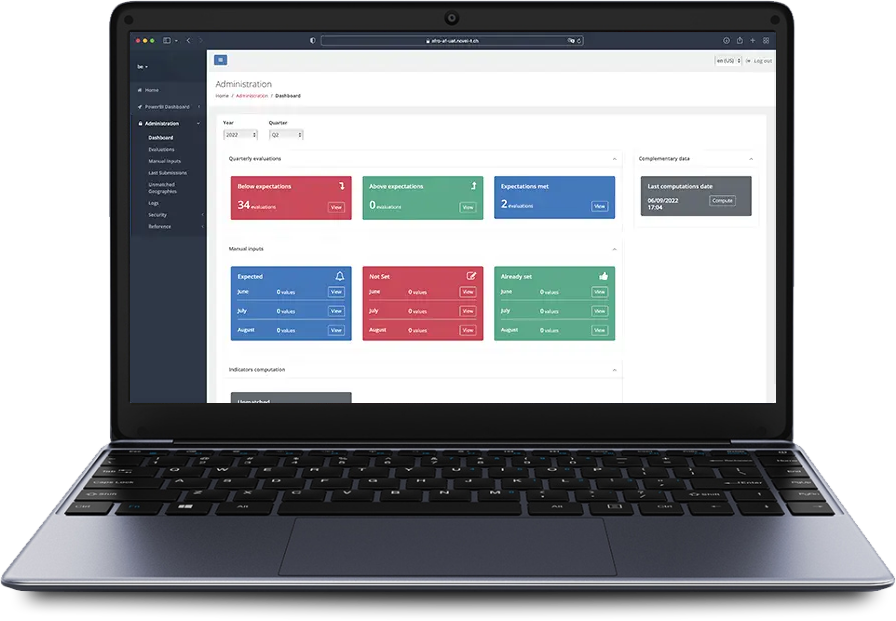
The intelligent scoring mechanism in the Accountability Framework factors in the program’s plan and does not penalize when there are no planned activities. The dashboard alerts users of missing data through a completeness score and allows data managers to resolve unknown geometries or to request data updates from countries.
6
400
34

Geographic deployment
Deployed in 6 countries, expanding to all 47 countries in AFRO
Context
After the successful eradication of wild polio virus from Africa in 2016, the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) recognized the need to maintain focus and performance for all polio activities to prevent the reappearance of the wild virus and to eradicate the vaccine derived polio viruses (cVDPVs) in the region. The first WHO accountability framework tool was developed in 2017 to support a systematic process of performance monitoring, evaluation, and feedback for both individuals and teams.
Raw data for polio activities at the country level was available. However, the burden of manual data collection and harmonization, along with the limitations of the desktop tools used to process the data made it difficult to produce analyses quickly and inform timely decisions.