Objectives
- Assess the risk for measles and rubella virus dissemination
- Identify at-risk areas to prioritize the implementation of corrective measures
- Validate surveillance and immunization data collected routinely
- Strengthen local capacities in the use and analysis of surveillance and immunization data
Description
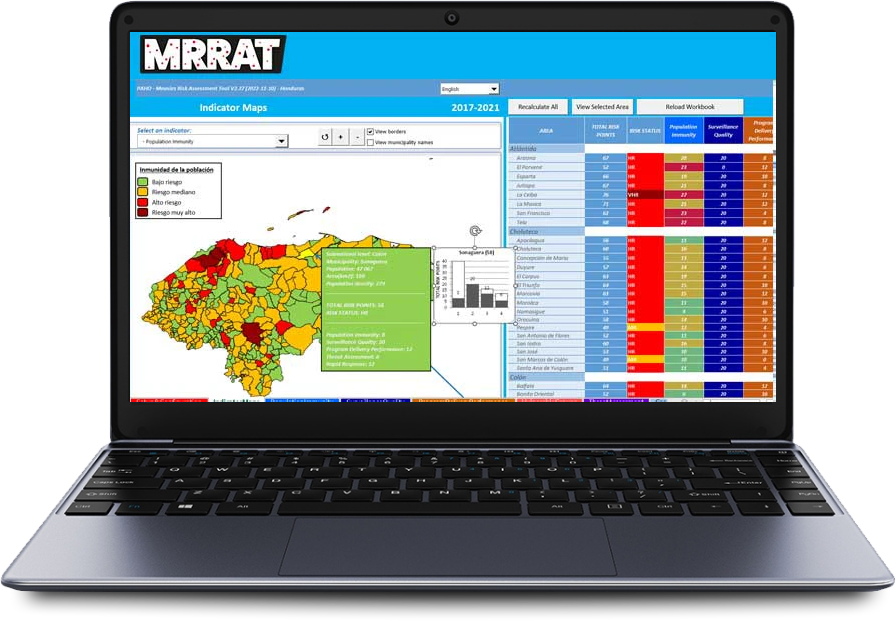
The Excel-based tool assesses subnational programmatic risk as the sum of indicator scores in four categories: population immunity, surveillance quality, program performance, and threat assessment. Each subnational area is assigned to a programmatic risk category of low, medium, high, or very high risk based on the overall risk score. Scoring for each indicator was developed based on expert consensus:
- Population immunity: Assesses measles susceptibility using subnational vaccination coverage data
- Surveillance quality: Evaluates the ability of a subnational area to detect and confirm cases rapidly and accurately.
- Program performance: Assesses specific aspects of routine immunization services, such as indicators for trends in coverage or dropout rates.
- Threat assessment: Accounts for factors that might influence the risk for measles virus exposure and transmission in the population.
The required data inputs include readily available and routinely collected data from the immunization and surveillance programs. Results are shown in table and map formats. Country reports can be created directly from the tool.
The tool is available in English, French, Spanish and Portuguese
+68
>30
+350

Geographic deployment
5 continents: Africa, Asia, Europe, North America, South America
Context
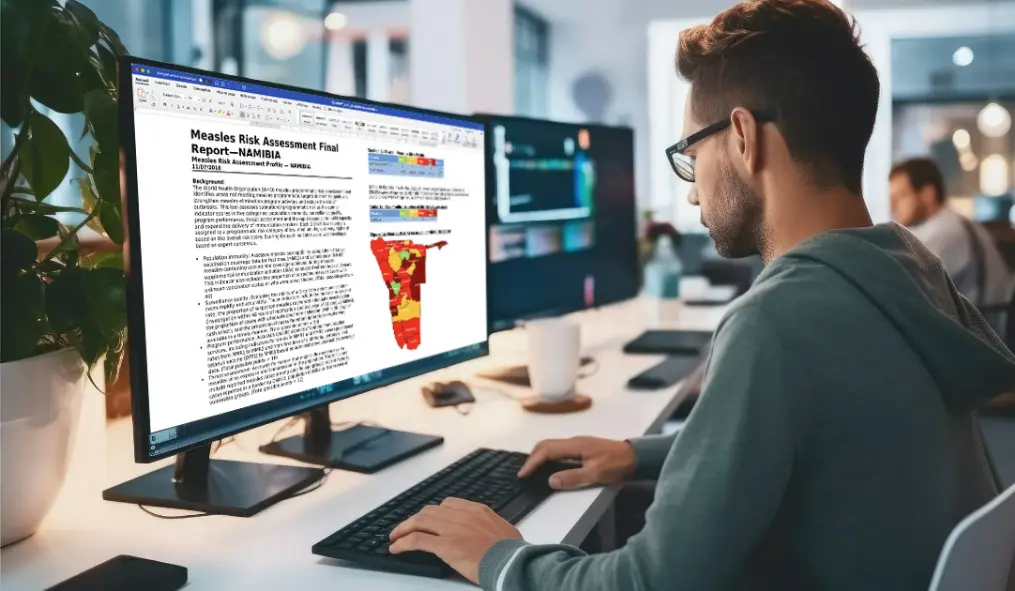
The World Health Organization (WHO) measles programmatic risk assessment tool has been developed to prioritize measles elimination efforts by identifying at-risk areas at the subnational level that are off-track from meeting performance targets and require strengthening of programmatic efforts and reduce the risk of outbreaks.
It is intended to be used annually by national program managers to monitor implementation of measles elimination strategies within a country.
The results of the risk assessment tool would be used typically to:
- Advocate with policymakers to continue investing in elimination activities.
- Mobilize resources for implementing corrective actions.
- Prioritize local interventions.
- Incorporate them in the annual country sustainability plans for measles and rubella.
The tool is not meant to be used for predicting outbreaks, but rather for preventing virus spread if an importation occurs. Additionally, the results can be used for planning and implementing measles and rubella follow-up campaigns.
Before the introduction of the tool, the yearly Projection of the country assessment document was very manual, tedious and time consuming.